Abstract
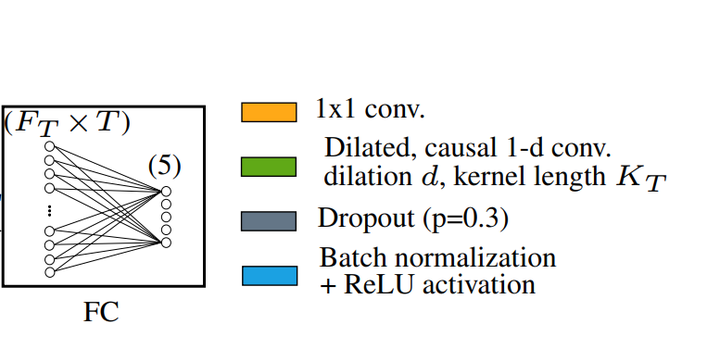
Personalized ubiquitous healthcare solutions require energy-efficient wearable platforms that provide an accurate classification of bio-signals while consuming low average power for long-term battery-operated use. Single lead electrocardiogram (ECG) signals provide the ability to detect, classify, and even predict cardiac arrhythmia. In this paper we propose a novel temporal convolutional network (TCN) that achieves high accuracy while still being feasible for wearable platform use. Experimental results on the ECG5000 dataset show that the TCN has a similar accuracy (94.2%) score as the state-of-the-art (SoA) network while achieving an improvement of 16.5% in the balanced accuracy score. This accurate classification is done with 27x fewer parameters and 37x less multiply-accumulate operations. We test our implementation on two publicly available platforms, the STM32L475, which is based on ARM Cortex M4F, and the GreenWaves Technologies GAP8 on the GAPuino board, based on 1+8 RISC-V CV32E40P cores. Measurements show that the GAP8 implementation respects the real-time constraints while consuming 0.10mJ per inference. With 9.91GMAC/s/W, it is 23.0x more energy-efficient and 46.85x faster than an implementation on the ARM Cortex M4F (0.43GMAC/s/W). Overall, we obtain 8.1% higher accuracy while consuming 19.6x less energy and being 35.1x faster compared to a previous SoA embedded implementation.
Supplementary code for the paper can be found here.